Version Control
The SORCER Project uses Git for version control. Git is a distributed revision control system with an emphasis on speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows. Git was initially designed and developed by Linus Torvalds for Linux kernel development in 2005, and has since become the most widely adopted version control system for software development.
Git supports rapid branching and merging, and includes specific tools for visualizing and navigating a non-linear development history. A core assumption in Git is that a change will be merged more often than it is written, as it is passed around various reviewers. Branches in git are very lightweight: A branch in git is only a reference to a single commit. With its parental commits, the full branch structure can be constructed.
Some data flows and storage levels in the Git revision control system. 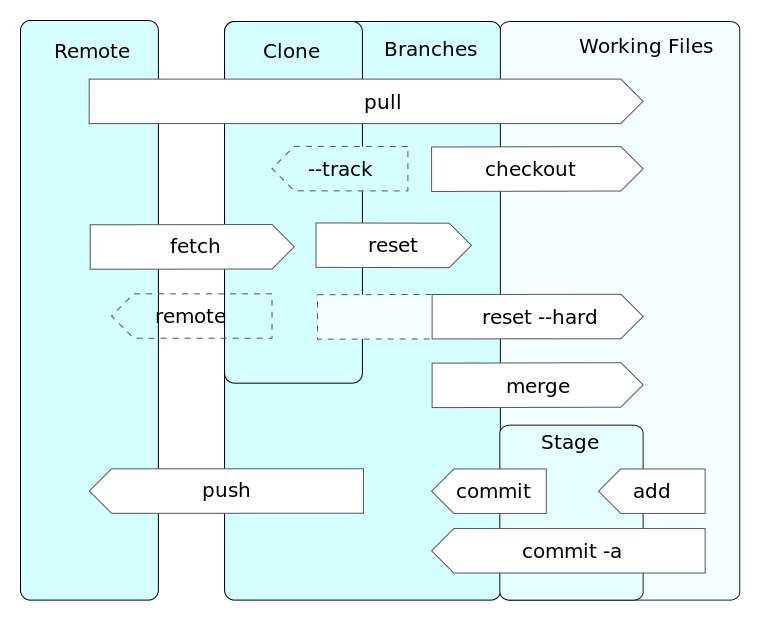
Check out the Git Cheat Sheet
Basic Git Workflow
- Checkout a repository
git clone username@host:/path/to/repository
- Add and Commit
You can propose changes (add it to the Index) usingorgit add
This is the first step in the basic git workflow. To actually commit these changes usegit add *
Now the file is committed to the HEAD, but not in your remote repository yet.git commit -m "Commit message"
- Pushing Changes
Your changes are now in the HEAD of your local working copy. To send those changes to your remote repository, executeChange master to whatever branch you want to push your changes to.git push origin master
- Update
To update your local repository to the newest commit, executegit pull
- Merge
To merge another branch into your active branch (e.g. master), useGit tries to auto-merge changes. Unfortunately, this is not always possible and results in conflicts. You are responsible to merge those conflicts manually by editing the files shown by git. After changing, you need to mark them as merged withgit merge <branch>
git add <filename>
